Invest in the future
The procedures established today for developing complex mechatronic systems are often stretched to their limits. ITQ has been involved in a multitude of research projects for more than 20 years, with the goal of coping with the increasing importance of interdisciplinary development. For it is important for the continuing ability of German companies to compete on the international market to give new directions and new impetus on the research sector. For this reason, we participate in the planning and implementation of research projects.
Research Projects
Benefits
Developing the technologies of the future
Nowadays, new technologies are developing faster than ever. Shape the future for sustainable improvements with us!
Cross-industry networking
In our research projects, we operate in a network. Benefit from a wide range of branch know-how from our partners.
Shaping research & teaching
Support us in shaping the future and promote with us young talents and formative minds of the future.
Interdisciplinary knowledge transfer
Receive new impulses as a partner in future research projects and share your knowledge. We network you with other disciplines.
BASYS 4.2 – Convertible Production
Reference Architecture for Production Systems Enables the Transition to Industrie 4.0
The focus of the BaSys 4.2 (Basissystem Industrie 4.0) research project is on the further development of the open-source BaSys 4.0 middleware and the Basyx framework as a reference architecture for adaptable Industrie 4.0 production. The aim is to drive forward the practical realization of the fourth industrial revolution. In addition, methods of end-to-end digital engineering based on a digital twin are to be researched.
Continuous engineering should enable the transformation of production in relation to the manufactured product, the production resources and the production process. Plant downtimes are to be optimized for continuous production with batch size 1. To achieve this, the focus is on edge computing, model-based capability description and the virtualization of production.
More Information:
ROMAFO – Moldable Parts in Robots

Assembly of Moldable Components with Robot Assistance and Machine Vision
The research project RoMaFo (Roboterassistenzsystem und maschinelles Sehen zur Montage von formlabilen Bauteilen bei kundenindividuellen Produkten) focuses on the development of a robot assistance system for the automated assembly of moldable linear components. To this end, a mechatronic gripping system is to be developed that uses machine vision to enable automated programming of conventional industrial robots. The newly developed methods, approaches and solutions create great potential for increasing efficiency and ergonomics during the assembly of dimensionally unstable linear components, as such processes still have to be carried out mainly manually in today’s production.
Generally applicable gripping and plugging strategies are to be developed using the example of automated cable assembly. For successful use in practice, the entire process chain of an assembly process is considered, so that quality inspection using additional sensor technology is also taken into account.
More Information:
SMARTB4P – Smart battery control

Smart Battery Control for Production
The research project SmartB4P (Smart battery control for production) investigates a self-learning operating strategy for electricity storage systems in manufacturing companies to reduce electricity costs. The focus of the intelligent control system is on maximizing self-consumption, avoiding expensive peak loads and efficiently controlling the battery storage system in combination with loads of the production system that can be switched off, taking battery ageing into account. In this project, ITQ GmbH is concentrating on the development of software solutions and automation technologies for machine control.
More Information:
RETHINK – Innovative Remanufacturing

Integrating Closed-Loop Processes into Existing Production Systems
The research project RETHINK (Remanufacturing for the industrial circular economy in SMEs using existing systems) is designed to enable companies to achieve more sustainable and resource-efficient production. By integrating closed-loop processes, especially remanufacturing, into existing production systems, plant capacity is better utilized and downtimes are avoided. In this project, ITQ GmbH is focusing on the use of innovative digital technologies for planning and controlling closed-loop processes. The use of a digital twin, which represents a flexible and hybrid disassembly and reassembly line, plays a central role here.
BERDIBA – Digital railroad operation

Automated Driving by Rail
In the project BerDiBa (Berliner Digitaler Bahnbetrieb) a consortium of 12 partners is developing technologies to digitalize rail transport and promote sustainable and environmentally friendly mobility. The focus is on three aspects to make digital rail operations safer and more efficient: driverless trains, automatically scheduled maintenance and automated remote control. ITQ GmbH is involved in the field of mechatronic development processes, the design of a digital twin and virtual commissioning. The project is co-financed by the European Union.
More Information:
KIRO – AI based robots
AI-based Robot Applications for Easy Scaling and Optimized Utilization
The research project KIRO (KI-basierte Roboterapplikationen) is dedicated to simplifying the realization of robot applications. By reducing the amount of expert knowledge, work and time required, the aim is to enable companies to quickly and easily deploy and scale up a wide range of robot applications in a multi-variant production environment. ITQ GmbH assumes responsibility for conceptualizing the development framework for robot applications and ensuring a structured approach from a mechatronic perspective.
More Information:
INTERACDT – Digital system twin

Interactive Digital Twin for Optimized Planning of Automated Sroduction Systems
InterAcDT (Interactive-collaborative Digital Twin) extends the digital planning and optimization of production facilities through the targeted further development and integration of technologies in the field of digital twins. With the help of AI-based optimization algorithms, innovative interaction methods and web-based provision, the digital plant twin is made accessible to a wide range of users. The collaborative use of the digital plant twin enables improved planning quality and economical production of new drive technologies. ITQ GmbH is involved in software integration for the operation of digital twins, interface development and implementation, spatial computing and the development of demonstrators with VR/AR interaction.
More Information:
SPIKE – Innovative AI pipelines

Cross-Phase Development of User Interfaces
The focus of the research project SPIKe (Smart process, product and service innovation through AI pipelines for established companies) is the sustainable development of intelligent demonstrators through AI pipelines for manufacturing companies. In addition, a reference model for AI pipelines is to be designed and iteratively developed to ensure technically sound development and easy transferability to other use cases. ITQ GmbH is designing a complex, cross-disciplinary system and brings expertise in AI-based process optimization as well as in the development of data pipelines in the production environment and in the simulation-driven development of mechatronic systems to the project.
SAFETRAIN – AI in driverless train

Safe AI in driverless Regional Trains
In the project safe.trAIn (safe AI for driverless regional trains) the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in rail transportation is being researched. The combination of AI with the safety aspects of rail transport will be put into practice using the example of the driverless regional train. This involves researching test methods and tools for AI-based approaches and developing and validating a GoA4 system in a virtual test field. ITQ GmbH takes on the task of deriving reliable evaluation options for the explainability of AI-based solutions for object recognition in the field of rail vehicles and other industrial applications.
More Information:
AUTODIS – Sustainable Circular Economy
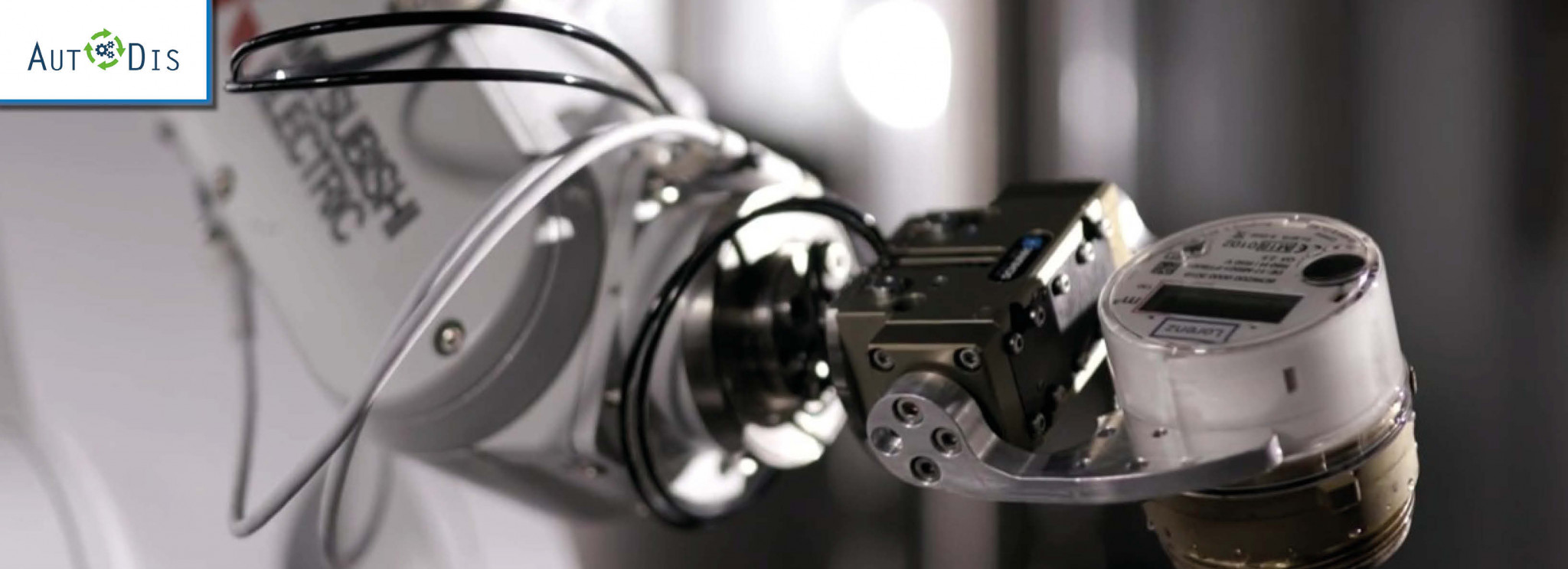

Automated Dismantling Processes and Component-by-Component Processing of Returned Products
With the research project Autodis (Automated disassembly) ITQ GmbH is driving the development of automated and intelligently networked dismantling of circular smart meter products in the spirit of the circular economy. Using the example of smart water meters, engineers and scientists from ITQ GmbH, TUM fml – future.meets.logistics and Lorenz are working on the automation potential of dismantling processes and the component-by-component processing of smart meter return products in the Autodis research project. The reuse of products, their maintenance and their recycling are important for the manufacturing industry in order to use resources more efficiently and contribute to an environmentally conscious circular economy.
More Information:
CraCoSu – Programming with Minecraft

Where Technology Meets Creativity: Exploring Sustainability with Minecraft
The research project CraCoSu (Craft & Code for Sustainability) is an initiative aimed at strengthening STEM education. In collaboration with Rhine-Waal University of Applied Sciences, ITQ GmbH develops hands-on educational formats that merge technological skills with creative expression. By combining programming with practical, action-based learning, students discover how to design innovative solutions to ecological and societal challenges using digital technologies—such as the Internet of Things, AI, or Open-Source Software. CraCoSu is part of Pakt für Informatik 2.0, an initiative launched by the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The project is co-funded by the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) or the Just Transition Fund (JTF).
More Information:
OUTDOC

Improving the Employability of Doctorates in Emerging Areas
The European project OUTDOC (Outplacement support for doctorates in emerging areas) is financed by Erasmus+ programme and coordinated by the University of Salamanca in Spain. It is aimed at improving the employability of doctorates in emerging areas. The main study goal was to reduce the mismatch between employers’ demands and expertise of doctorates while identifying employers’ needs. More than 250 companies from several European countries have participated in a query in order to find the most valuable skills for employers. The collected data will be used to develop an online soft skills training that will increase employability of doctorates in the industry.
More Information:
ECO MODE CONTROLLER

Energy-Efficient Process Control for Calenders
Because of increasing energy costs, a growing market for concepts for improving the energy efficiency of plants has emerged. The ECO MODE CONTROLLER project’s aim is the development of a more energy-efficient process control for plastic calenders, which is to be marketed later as a service by the companies involved. The unique selling point is the combination of high energy-saving potential, excellent integrability with existing plants, and low investment needs.
NUCLEI

Building Networks for Innovative Technology Transfer between Middle-European Industry and Trade Associations
The purpose of the international research project NUCLEI is to replace outdated international management models with a “local” approach to technology by a transnational knowledge pool in order to support progressive fabrication innovations beyond regional borders. This not only increases economic interlacing but also stimulates more effective transnational value-added chains in the automotive and electrical industry, the IT sector, robotics, and mechanical automation.
More Information:
MEPROMA

Mechatronic Engineering for Efficient Product Development in Mechanical Engineering
The currently existing approaches for mechatronic engineering often lack clear connection to practical application. The research project MEPROMA aims to clearly frame requirements for methods and tools using application scenarios. The foundation for this is the process areas and activities in mechatronic engineering which have been identified in previous research projects. This ensures that future generations of tools and methods fulfil the requirements of innovative product development and can be used in daily practice.
CyProS

Productivity and Flexibility Increase by Integration of Intelligent Systems in the Factory
The goal of the research project CyProS is to develop a representative spectrum of cyber-physical system modules and to create a conceptual and methodical foundation for their use in real production environments. ITQ is intensively involved in the generation of development methods for cyber-physical systems. Imaging cyber-physical systems, including their functions, components, and interfaces, is a key aspect.
AKOMI

Automated Configuration in Microsystems Technology
The main goal of the research project AKOMI is to increase the mutability of production plants. To achieve that, new methods for automatic configuration of microsystems components must be researched and implemented – that way the specialist effort for integration, configuration, and calibration of means of production in microsystems technology is reduced and reuse of means of production enhanced by appropriate modularization.
BESTVOR

Operational Introduction Strategies for Application-Oriented Process Model
The foundation of every improvement process is recording the current state. For that reason, a central element of the research project BESTVOR is an assessment method (self-assessment) which can determine the central fields of action for improving the development process in a company within a few hours. Based on the findings from the self-assessment, concrete recommendations are given on which actions to take. The foundation for the evaluation of processes and action recommendations is the results of previous research projects as well as already-published VDMA guidelines and, last not least, the experience of notable mechanical engineering companies which have participated in BESTVOR (2006-2009).
PEBEMA
Phase-Overlapping Development of User Interfaces in Mechanical Engineering
Current trends in the context of digitalization and “Industry 4.0“ make the operation of mechatronic systems more and more complex. To meet this challenge, utilizable systems are needed which the operators can master without problems. This can be achieved if the role of the operator is continuously taken into account when developing mechatronic systems. To this purpose, an interdisciplinary consortium has compiled a reference model for user-centered development of user interfaces of mechatronic systems within the research project PEBeMA.
Get in contact with us!
Make an appointment with us to find a suitable solution
for your project together.